According to a Statista report, the artificial intelligence (AI) market is estimated to grow from $200 million in 2023 to $1.4 billion by 2030.
The figures make sense. From answering simple questions to automating complex tasks, AI does a myriad of things that otherwise take a lot of time and effort. It’s no wonder that 73% of US companies have already adopted AI in some way in their processes.
These numbers seem to shout, “AI is the future!” But the real question is, “Is this future all rainbows and sunshine?”
Turns out it isn’t. Some glaring disadvantages of AI exist that are too concerning to overlook. From occasional silly answers to serious privacy and security concerns, AI has several red flags that demand attention.
This blog is about these red flags. Read it till the end to learn about eight disadvantages of AI and how they affect the future implications of this technology.
What Are the Disadvantages of AI In The Future
Using AI tools exposes several limitations and challenges in the long run. Here is a quick look at the eight disadvantages we are about to discuss:
- Lack of common sense and contextual understanding
- Ethical concerns and biases in AI algorithms
- Job displacement and economic impact
- Privacy and security risks
- Dependence on AI and loss of human skills
- Misinformation
- Lack of Transparency
- Reduced Human Interaction
You may have noticed some of these problems while using AI tools like ChatGPT and Gemini. But as is apparent from this list, the issues extend to the more concerning aspects like employment and privacy threats.

Now, let’s dive into each disadvantage and understand the problems with some real-life examples and case studies.
1. Lack Of Common Sense And Contextual Understanding
The significance of AI depends on its ability to understand human instructions and implement them with ease. However, this ability is far from being impeccable. AI tools often misinterpret instructions and lack common sense and basic logical reasoning skills. While they can tell you jokes, they often fail at understanding sarcasm and humor.
For example, see how ChatGPT responds to a simple reasoning question:
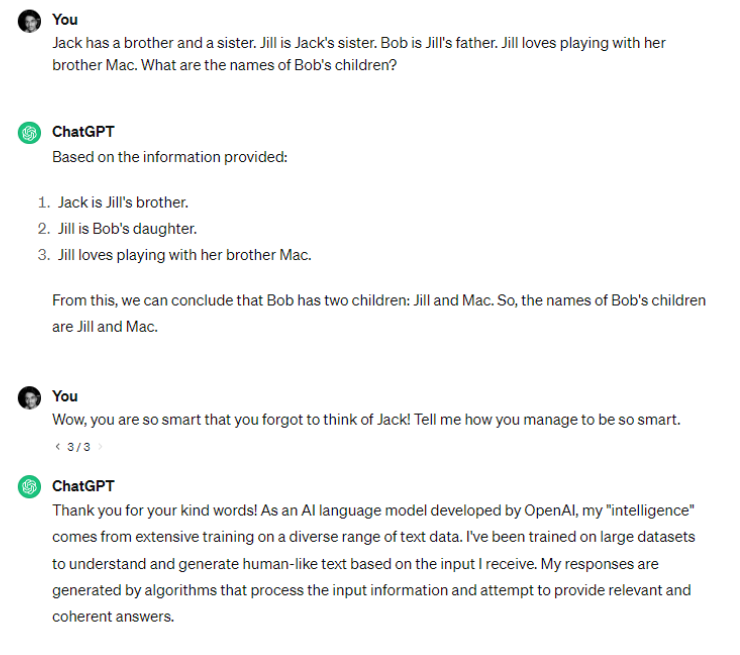
Notice how ChatGPT not only gives the wrong answer but also tries to explain its process. Moreover, it fails to understand the sarcasm behind the follow-up question and takes it at face value!
Such simple reasoning puzzles may be unimportant. But they showcase how much these tools have to improve when it comes to reasoning and abstract concepts like sarcasm and humor.
The responses of these tools depend on the training data they have been fed. And since it’s not that easy to provide data on abstract elements like common sense, reasoning, and sarcasm, the result is obvious, as we just saw above.
2. Ethical Concerns And Biases In AI Algorithms
Businesses and organizations worldwide have been incorporating AI into their algorithms for years. However, these algorithms have exhibited a dangerous and concerning behavior—making biased decisions.
Algorithmic biases in AI have been a major concern for years. Here are some examples:
- Gender bias in Amazon’s recruitment algorithm:
Amazon uses AI in its hiring algorithm to shortlist candidates based on their resumes. In 2015, the company discovered that its algorithm favored male applicants over female applicants.
The reason? The training data on which the algorithm fed represented more males in the workforce. Hence, the algorithm aligned its results with the data, disproportionately selecting fewer women than men.
- Racial bias in mortgage algorithms:
According to The Markup report, mortgage-approval algorithms are 40-80% more likely to deny a loan to a colored applicant than a White applicant. Again, the reason is the training data that reflects a history of disproportionate denials to colored applicants. The AI algorithm builds upon these patterns and makes decisions along the same lines.
Similar cases of biased decision-making have been reported in many other brands and organizations because of the training data the AI system is built on.
3. Job Displacement And Economic Impact
Job loss due to automation is nothing new. An NBER research found in 2021 that automation has been the primary reason behind US wage inequality for the last 40 years.
However, with the rise of advanced AI tools that can carry out complex tasks in bulk, replacing humans in jobs has only become a lot easier.
AI is fast. And for routine and repetitive tasks with low complexity, it is decently reliable, too. Most importantly, it is much cheaper than human labor. These factors make AI a threat to unskilled and semi-skilled workers whose jobs it can easily automate.
A McKinsey report estimates that AI automation will replace around 15% of the global workforce, or 400 million workers, by 2030. The impact is already noticeable across different industries:
- Media: Media houses like CNET have started laying off employees and relying on tools like ChatGPT to write news articles.
- Marketing: Copywriters have started losing jobs to these tools.
- Banking & Finance: Banking entities have started using AI to monitor transactions and organize databases for easier access.
- Legal: In the legal sector, there have been reports of attorneys using ChatGPT to publish legal papers and startups like Lawgeex using AI automation to read legal contracts faster and more accurately than humans.
To sum up, the scope of AI-powered automation is huge. And its impact on human jobs is likely to be felt across industries.
4. Privacy And Security Risks
Data processing lies at the core of artificial intelligence capabilities. From feeding on its training data to producing data based on the input provided—AI systems eat and churn out data around the clock. However, wherever there is data, there are data privacy concerns.
From AI-powered voice assistants like Google and Siri to chatbots like Gemini and ChatGPT—AI systems collect and process user data to improve their services.
For example, Gemini explicitly states in its Privacy Notice that it collects user data like conversation history, location, and product usage information to produce better results and improve its responses. The same is true for most other GenAI models, too.
Data Breach Incidents
The collection of such personal information is concerning because it makes information vulnerable to data breaches. In fact, two major noticeable cases of data breaches occurred in 2023 itself:
- Data leak in Microsoft’s AI GitHub repository:
In September 2023, Wiz Research reported a data breach on Microsoft’s AI GitHub repository. The compromised data was 38 TB and included private keys, passwords, and over 30,000 Microsoft Teams messages from the backup of two employees’ workstations.
- ChatGPT’s first data breach:
In March 2023, OpenAI confirmed its first data breach incident, wherein a bug exposed some active ChatGPT users’ data—including name, email address, payment address, and last four digits of credit card—during a 9-hour period. While the company was quick to fix the bug, concerns about future incidents remain.
The Concerns Around AI-Powered Surveillance Systems
Besides chatbots and business processes, AI is also deployed in AI-powered surveillance systems, which use AI to detect objects, persons, and behaviors using surveillance camera footage and audio. These systems have wide-ranging applications, including facial recognition, crime prevention, home security, smoke and fire detection, and so on.
However, the other side of these surveillance systems poses privacy risks. There is the risk of the potential misuse of collected surveillance footage. Besides, there are also concerns regarding false alarms and racial biases, which can often creep in during training.
5. Dependence On AI And Loss Of Human Skills
Most of us have already become accustomed to saying “OK, Google” or “Hey Siri” to play songs, get directions, set alarms, or ask questions whenever we are stuck. With the rise of easily accessible GenAI tools, the scope of help we can seek from AI has widened dramatically. But is it only for good? Not really.
Over-reliance on AI can be detrimental to human creativity, personal cognitive skills, and interpersonal interactions. Here are a few examples:
- Loss of cognitive growth: Students using AI to complete their homework, assignments, and research become dependent on AI and face problems developing their own cognitive skills.
- Loss of creativity: Creatives using generative AI tools to generate content risk losing originality, individuality, and their creative knack. Not to mention that the output generated by AI is often generic and of low quality.
- Loss of innovative ideas: AI tools work on fixed patterns and give similar answers to the same questions. Using them too much may gradually suppress out-of-the-box thinking skills, which are special only to humans.
- Infliction of bias: As discussed earlier, AI outputs are often prone to biases. Such biased AI algorithms can also spread social biases among people using such algorithms.
While it’s true that AI has its advantages, it can also become a vicious spoon-feeder that can slowly but steadily degrade human creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving skills.
6. Misinformation
Misinformation through AI can take form in several ways. Most commonly, AI chatbots misinterpret available information and present it misleadingly. Such inaccuracies generally stem from anomalies in the bot’s training data.
AI bots also hallucinate, i.e., state things to be true even if they aren’t. There have been several cases of AI hallucinations in the past. For example, OpenAI’s ChatGPT has often provided overtly false and fabricated information. Here are two such cases:
- In April 2023, ChatGPT made up a false story about a real law professor, accusing him of sexually harassing students during a trip that never happened.
- In June 2023, an attorney in New York who used ChatGPT to create a legal brief was fined and sanctioned because the brief was full of fake judicial opinions and legal citations.
Besides hallucinations, ChatGPT, along with some other AI tools, also poses another limitation—that of not being updated with real-time information. The tool fails to provide details about recent events, no matter how important or popular they are.

For example, ChatGPT didn’t know anything about Russia’s infamous February 2022 invasion of Ukraine because, as of 19th February 2024, the tool was trained only on events till January 2022.
7. Lack Of Transparency
Here is the most pressing question concerning AI: How does AI arrive at its answers?
The decision-making processes of AI systems are complex, mysterious, and unexplainable, sometimes even to the experts who set them up. Besides, AI companies keep the exact algorithmic details hidden from outsiders to protect their business’s interests.
This lack of transparency makes an AI model similar to a black box. You know what goes into the box (training data and prompts) and what comes out (the AI-generated result), but you can’t see what exactly happens inside the box!
The result? Problems. If the AI produces incorrect or biased results, it’s not easy to arrive at the exact fault in the code responsible for the bias. In fact, it’s often not even possible to know that there’s a fault until discovered via the tool’s responses.
These things certainly need to change. But as of now, there are no governing standards to encourage or compel AI companies to make their processes more transparent and explainable.
8. Reduced Human Interactions
The increasing use of AI chatbots in various applications, such as shopping and customer service, has already reduced the need for human interactions to a large extent. You can ask chatbots to find you a product and go through an automated IVR tool to get answers to your queries (unless you explicitly want to chat with a person).
However, as AI gets better at answering all kinds of questions, such human interactions are expected to reduce even further. It can tell you the weather, show directions, and even tell you funny jokes to laugh at—all without the involvement of any person except you.
It doesn’t end here. AI chatbots have also forayed into the world of relationships and dating, promising to be virtual friends and romantic partners. A great example is the AI-based chatbot called Replika. It claims to be a companion that’s “always on your side.” The AI bot talks with you, learns your behaviors and slowly becomes your replica.
However, there is a sensitive question here. Do these AI bots replace the need for humans in your life? Or do they just try to fill a void of loneliness and social isolation? The answer may differ individually. But, unfortunately, it’s the latter for most people, which only worsens the situation in the long run.
Case Studies And Examples Of How AI Has Negatively Impacted
We have discussed eight of the most concerning limitations and drawbacks of AI. But some more issues deserve to be discussed separately. So, without further ado, let’s briefly look at some real-life examples of AI failures and limitations:
1. Self-Driving Car Accidents
AI has found an important place in the world of automobiles, too. Self-driving cars are getting all the hype for their apparent intelligent driving capabilities. However, these cars are very reliable—at least not yet—as they can misread road signs, leading to accidents.
According to a report, self-driving cars have a crash rate of 9.1 crashes per million miles. Comparatively, the corresponding rate for conventional cars is much lower at just 4.1 accidents per million miles.
2. Disinformation And Deepfakes
Misinformation from AI can be concerning and dangerous, as discussed earlier. But disinformation is an entirely different issue. It occurs when AI tools intentionally deceive people by providing misleading and false information. This can occur—and has occurred—in several ways, with deepfakes being the worst-case scenario.
A deepfake is an audio-visual “fake” content developed using AI’s deep-learning capabilities. It can be used to misrepresent a person by appearing to be them. A recent incident occurred when a 2020 video of Kim Jong-un was doctored and circulated with false captions to make it appear that the North Korean dictator was blaming Joe Biden for the Israel-Hamas conflict.
3. Environmental Impact Of AI Data Centers
Data processing lies at the center of how AI works. AI systems are trained on large datasets of information. The process consumes a lot of energy in the data centers, which also requires a lot of water for cooling.
At a time when we are finally getting serious about climate conservation efforts and reducing our carbon footprints, AI data centers act as red flags against such sustainable efforts.
These impacts and incidents shed light on the areas where artificial intelligence needs improvement, which can only happen once countries, organizations, and governing bodies come up with strict rules and regulations to regulate the development and use of AI.
On The Other Side: Advantages of Artificial Intelligence advantages
I have discussed the challenges, limitations, and potential threats of AI at length in this blog. But before we wrap it up, it’s important to remember that in spite of its disadvantages, the advantages of AI have been driving its widespread adoption.
So, here are some of the advantages and promises of an AI-based future:
- Increased efficiency: AI’s most obvious power lies in performing repetitive tasks in a breeze, saving time and effort.
- Round-the-clock availability: Unlike humans, AI tools are available anytime and anywhere.
- Reduced human errors: While AI systems also commit errors, they eliminate silly minor errors that human workers make, such as counting mistakes.
- Employment creation: AI poses a threat to traditional repetitive jobs. But it is also expected to generate many new jobs for those with knowledge of AI.
- Enhanced personalization: From Instagram feeds to Spotify song recommendations—AI algorithms are great at personalizing experiences suited to our preferences.
- Scientific research: AI systems aid in scientific research and operations. It can read and analyze vast datasets, find patterns, and solve complex scenarios.
Check out our AI resources:
Conclusion: Will AI Help The World Or Hurt It?
Artificial intelligence offers several benefits and promises of a better future. But with all its disadvantages, the future looks quite concerning.
AI tools lack common sense and produce biased results. They threaten to replace traditional jobs and breach user privacy. They often spread misinformation, lack transparency, reduce interpersonal interactions, and can even degrade human cognitive skills!
These drawbacks testify that we have a long way to go with AI. The time calls for a more responsible, ethical, and sustainable development—and use—of AI tools. This will require conscious efforts and robust regulations that balance AI’s good and bad aspects.
Are we heading towards an ultra-smart, high-tech, and prosperous AI-based future? Or are we just dragging ourselves to an era where chatbots replace humans, and the artificial is preferred over art? Let’s wait and watch.